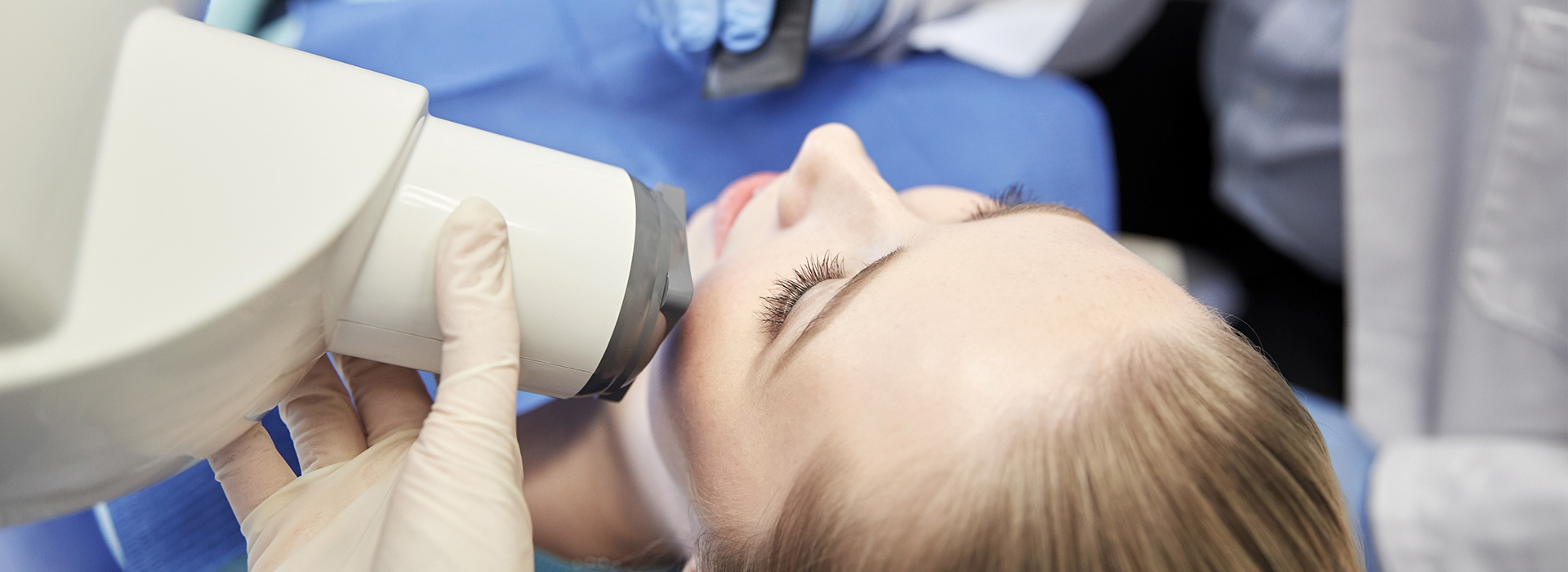
Digital radiography is the contemporary method of capturing dental images using electronic sensors and computer processing instead of traditional photographic film. The system converts X-ray energy into a digital signal that appears as a high-resolution image on a monitor within seconds. This change in workflow has reshaped how clinicians diagnose and plan care, allowing for more responsive examinations and clearer visual communication between practitioner and patient.
Although the basic purpose remains the same as film—revealing the structures beneath the enamel—digital systems add layers of utility. Images can be enhanced, magnified, and measured with precision tools that help clinicians identify early signs of decay, bone changes, and root issues that might not be obvious during a visual exam. The result is a more informed treatment process built on better visual evidence.
For patients, the experience feels faster and more informative. Instead of waiting minutes for film to develop, your dentist can review images immediately, explain what they show, and use them to illustrate recommended treatment paths. That immediacy makes appointments more productive and helps patients feel more involved in decisions about their oral health.
One of the most meaningful benefits of digital radiography is the reduction in radiation exposure compared with conventional film X-rays. Digital sensors are more sensitive to X-ray photons, which means diagnostic-quality images can be produced with a lower dose. This improvement aligns with modern safety principles that aim to minimize exposure while maintaining image clarity for accurate diagnosis.
Beyond the sensor technology itself, digital workflows make it easier to follow conservative imaging protocols. Dentists can take targeted images rather than broad, overlapping shots, and software allows for adjustments that reduce the need for repeat exposures. These combined features contribute to a safer imaging environment for patients of all ages.
Safety also extends to how images are handled. Digital files eliminate the need for chemical development and film storage, removing environmental concerns connected with processing solutions and physical waste. The result is a cleaner, more responsible approach to diagnostic imaging that benefits both patients and the practice.
Digital radiographs offer clinical advantages that go beyond convenience. High-resolution images can be enhanced with contrast and brightness tools, and clinicians can zoom in to evaluate fine details. These capabilities make it easier to detect small carious lesions, evaluate the integrity of restorations, and assess bone levels around teeth and implants with greater confidence.
Measurements taken directly on the digital image improve the precision of treatment planning. Whether preparing for root canal therapy, planning implant placement, or monitoring periodontal changes over time, the ability to measure distances and angles with software tools supports predictable outcomes. This objective data helps clinicians create tailored treatment plans that address each patient’s unique anatomy.
Because images are instantly available, clinical teams can review findings together and consult with specialists more efficiently when needed. That collaborative advantage shortens the time from detection to treatment and improves coordinated care across providers, all founded on the same clear digital reference.
Digital radiography streamlines administrative tasks and strengthens recordkeeping. Images are stored directly in the patient’s electronic file, which simplifies retrieval during follow-up visits and provides a consistent visual history of oral health. This continuity helps clinicians track changes over months or years without sorting through boxes of film.
Secure electronic storage also makes it practical to share images with other providers when a referral is needed. Rather than mailing physical X-rays or relying on patients to transport films, clinicians can transmit high-quality images quickly and securely, accelerating consultations and second opinions while reducing logistical barriers.
From an office operations standpoint, the reduced need for physical storage space and chemical supplies lowers overhead and minimizes environmental impact. Those operational efficiencies free up clinical time for patient care and help maintain a modern, organized practice environment.
Undergoing a digital X-ray is similar in comfort to traditional imaging, but there are a few notable differences in patient experience. A small, thin sensor is positioned in the mouth to capture intraoral images; for extraoral views, a stationary digital detector photographs the jaws from outside. Most patients find these sensors comfortable, and the quick capture time helps keep appointments brief.
After images are taken, your dentist will review them with you on a monitor. This visual review is an opportunity to ask questions and understand the specific findings—whether it’s an area of early decay, the condition of a filling, or the bone support around a tooth. Seeing the image makes explanations more concrete and helps patients participate meaningfully in treatment decisions.
At the office of Schneider Family & Cosmetic Dentistry, digital imaging is part of a commitment to precise, patient-focused care. If you have concerns about radiation exposure, image privacy, or what to expect during imaging, your dental team can explain how technology is used safely and how images are protected within your health record.
We encourage patients to view digital radiography as a collaboration tool: it improves diagnostic clarity, enhances communication, and supports safer, more efficient care. Contact us to learn more about how digital imaging is used during appointments and how it contributes to comprehensive oral health management.
Digital radiography uses electronic sensors to capture X-ray energy and convert it into a digital image that appears on a monitor within seconds. Sensors detect X-ray photons and send a signal to computer software that reconstructs a high-resolution image for immediate review. This process replaces film development and lets clinicians view, enhance, and store images almost instantly.
The quick availability of images supports more efficient appointments and clearer communication between clinician and patient. Software tools allow clinicians to adjust contrast, zoom and measure directly on the image to evaluate fine details. Because files are digital, they can be retained in the patient record and compared over time to track changes.
Digital radiography eliminates chemical processing and physical film by using electronic detectors that produce an image immediately after exposure. The sensors are generally more sensitive than film, which reduces the need for repeat exposures and improves workflow in the operatory. Digital images can also be enhanced and measured with software tools that are not available with conventional film.
Another key difference is storage and sharing: digital files are archived in the patient record and transmitted electronically to specialists when needed, while film requires physical handling and storage. Environmental benefits are notable because digital systems remove the need for developing chemicals and film disposal. These operational advantages help practices maintain a modern, efficient care environment.
Digital radiography typically requires less radiation than conventional film because sensors are more efficient at capturing X-ray photons, which supports modern safety principles that aim to minimize exposure. Clinicians follow conservative imaging protocols and use collimation and proper positioning to limit the exposed area, reducing unnecessary dose. For younger patients, reduced exposure and faster capture times make digital imaging an appropriate diagnostic tool when clinically indicated.
If you have concerns about radiation exposure, you should discuss them with your dental team so they can explain the steps taken to minimize dose and why a particular image is needed. Pregnant patients or those with special medical conditions should inform the staff so the team can adapt imaging protocols and take additional precautions. Overall, digital technology facilitates safer imaging while preserving diagnostic quality.
Digital radiographs can show structures beneath the enamel such as interproximal decay, the extent of restorations, root anatomy, and bone levels that are not visible during a clinical exam. These images help detect early-stage caries, periapical pathology, and periodontal bone loss so clinicians can intervene before issues progress. Enhanced imaging and magnification make it easier to identify subtle changes that might otherwise be missed.
For restorative and endodontic care, radiographs clarify the relationship between teeth and surrounding bone and reveal root morphology and canal anatomy. In implant planning and monitoring, radiographs help assess bone support and detect changes over time. This hidden information supports more precise diagnoses and tailored treatment recommendations.
Digital radiography provides high-resolution images that clinicians can adjust for contrast and brightness, measure precisely, and magnify to evaluate fine details important for diagnosis. Measurement tools on the software help determine distances and angles that are useful for procedures such as root canal therapy, crown fitting and evaluating bone levels around teeth and implants. These objective data points contribute to predictable, anatomy-informed treatment planning.
Because images are immediately available, the clinical team can review findings together and consult with specialists without delay, which improves coordination of care. Digital archives also allow comparison across visits to monitor healing or progression, supporting evidence-based decisions. Overall, the technology enhances diagnostic confidence and helps tailor care to each patient’s needs.
During an intraoral digital X-ray, a small, thin sensor will be positioned inside your mouth to capture images of individual teeth or groups of teeth, and the capture time is very short. For extraoral views, a stationary detector or panoramic unit records broader images of the jaws and facial structures while you remain still for a few seconds. Most patients find the sensors comfortable and appreciate that images appear on a monitor right away for instant review.
After capture, your dentist or hygienist will review the images with you on-screen and explain any findings using the enlarged and enhanced views. This screen-based review is an opportunity to ask questions and better understand recommended care. At the office of Schneider Family & Cosmetic Dentistry in Mooresville, the team uses these visual tools to make explanations clear and to involve patients in treatment decisions.
Digital radiographs are stored electronically within the patient’s health record, which simplifies retrieval and provides a continuous visual history of oral health. Offices typically use secure, encrypted systems and HIPAA-aligned policies to protect access to digital files and to ensure that images are shared only with authorized providers. Electronic storage reduces the risk of lost or damaged films and supports efficient recordkeeping.
When referrals or specialist consultations are required, clinicians can transmit high-quality images quickly using secure methods, avoiding the need for physical film transfer. Patients who request copies of their images for personal records or specialist visits can receive them in digital format consistent with privacy safeguards. These practices enhance both convenience and confidentiality.
Digital radiographs play an important role in initial implant evaluation by showing bone levels, adjacent tooth roots and preliminary anatomical relationships needed for implant planning. Software measurement tools help estimate available bone height and location relative to neighboring structures, which supports surgical planning and prosthetic design. For many routine cases, high-quality intraoral and panoramic images provide the information needed to proceed safely.
For complex three-dimensional planning or when bone anatomy must be evaluated in cross-section, clinicians often complement digital radiographs with cone beam computed tomography (CBCT) for more detailed 3D views. Together, 2D digital radiographs and 3D imaging provide a comprehensive diagnostic picture that supports safe, predictable surgical and restorative outcomes. Follow-up radiographs are also useful to monitor integration and long-term stability of implants.
One of the main advantages of digital radiography is immediacy: images are available for review within seconds of capture, allowing the dentist to discuss findings during the same visit. Clinicians typically use the enlarged on-screen images to point out areas of concern, explain clinical implications and outline recommended next steps. This real-time review makes appointments more informative and helps patients understand their oral health status clearly.
If further consultation with a specialist is needed, digital files can be transmitted quickly to facilitate timely second opinions and collaborative planning. The ability to review images together as a team shortens the time from detection to treatment. Patients benefit from faster decision-making and coordinated care based on the same clear visual evidence.
The adoption of digital radiography supports better diagnostic clarity, faster appointments and improved patient communication, which are central to modern dental care. Digital systems reduce radiation exposure when used with conservative protocols, eliminate chemical processing and streamline recordkeeping, contributing to both patient safety and environmental responsibility. These operational benefits help the clinical team focus more time on individualized patient care.
At the office of Schneider Family & Cosmetic Dentistry, digital imaging is used to enhance clinical decision-making and to visually involve patients in their treatment plans. By combining high-quality images with secure electronic records and collaborative workflows, the practice delivers care that is precise, efficient and easier for patients to understand. If you have questions about how imaging is used during your visit, the team can explain the specific protocols and benefits for your care.

Ready to schedule your next dental appointment or have questions about our services?
Contacting Schneider Family & Cosmetic Dentistry is easy! Our friendly staff is available to assist you with scheduling appointments, answering inquiries about treatment options, and addressing any concerns you may have. Whether you prefer to give us a call, send us an email, or fill out our convenient online contact form, we're here to help. Don't wait to take the first step towards achieving the smile of your dreams – reach out to us today and discover the difference personalized dental care can make.